Extraction
RECOVERY OF HIGH BOILING SOLVENTS FROM WASTE WATER
DESTROY OR RECOVER?
 Industrial waste water often contains high boiling solvents, such as phenol or dichlorobenzene, and so cannot be discharged into a sewage treatment plant without reprocessing and cleaning. Since destruction through burning is not only a bad alternative ecologically but also too costly due to the high water content, the preferred way is phenol recovery with simultaneous cleaning of the waste water until it can be discharged into the sewage treatment plant. The example of phenol is used to describe the method used repeatedly by SCS
Industrial waste water often contains high boiling solvents, such as phenol or dichlorobenzene, and so cannot be discharged into a sewage treatment plant without reprocessing and cleaning. Since destruction through burning is not only a bad alternative ecologically but also too costly due to the high water content, the preferred way is phenol recovery with simultaneous cleaning of the waste water until it can be discharged into the sewage treatment plant. The example of phenol is used to describe the method used repeatedly by SCS
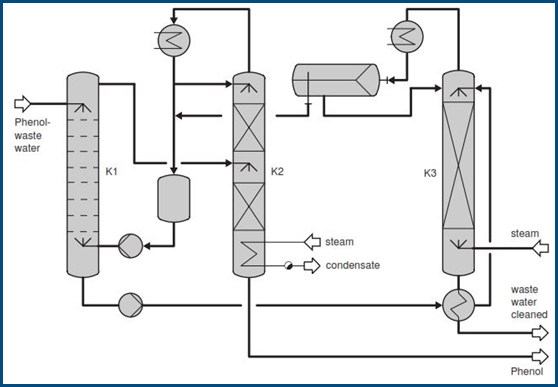
The phenol content, which depends on the process, is normally 2-12%. The low phenol concentrations eliminate separation by distillation, in which the water is evaporated out, due to the high energy requirements. Here, extraction offers the decisive advantage. Methylisobutylketone (MIBK), an extracting agent, removes phenol from the waste water in the extraction column K1. The charged extracting agent is cleaned again in the distillation columnK2 and returned to the bottom of the extraction. The phenol accumulates in the bottom of the subsequent rectification (column K2) and can be used again in production.
While the waste water flowing out of the extraction K1 may be free of phenol, it carries along traces of the extracting agent, which are recovered in the stripper K3. The MIBK/water az eotrope accumulates at the head of the column, where it is separated in the separator B1 into the light MIBK phase and the heavy water phase. Since the distillation column K2 is operated without water, indirect heating is planned here, while direct steam can be introduced into the stripper.
